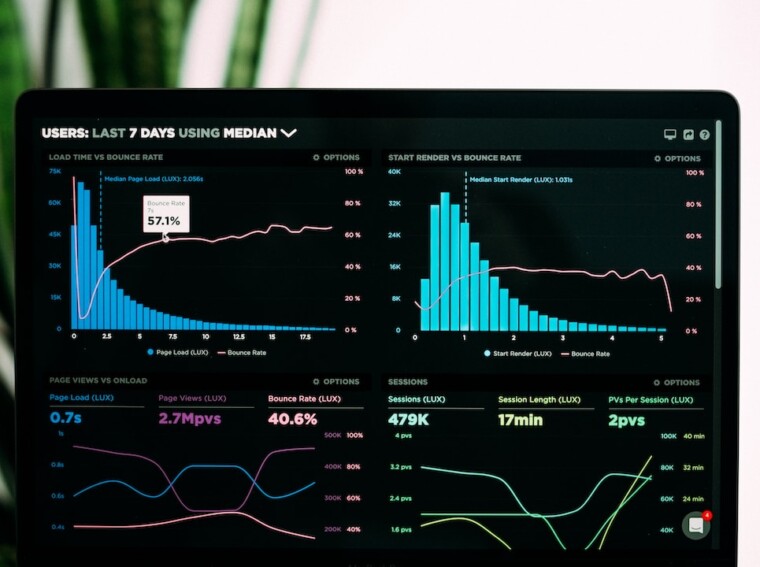
A simple graph can narrate a complex story understandably. One type of graph is a spline chart. Spline charts provide a dynamic data visualization, making it easier to understand trends and patterns. In this article, we’ll explore the ins and outs of a spline chart.
Understanding The Basics of a Spline Chart
To utilize a spline chart effectively, we must first understand what it is. A spline chart is a diagram that uses curved lines to represent data, especially data involving trends over time.
The special thing about spline charts is their ability to show the fluid movement of data. Regular line charts might appear jagged or disjointed, while spline charts provide a smoother and more organic look. This smoothens out any data inconsistencies and makes it easier for the viewer to follow trends and changes.
Creating a spline chart involves plotting points on a graph, with the x-axis typically representing time and the y-axis representing the data being studied. After plotting the points, a smooth curve is drawn to connect them, providing a visualization of the data’s change.
Any infographic should aim for two main properties: clarity and conciseness. Clarity in a spline chart means that the viewer should be able to understand the data.
Steps To Create a Clear And Concise Spline Chart
Creating a spline chart begins with data collection. Clearly, understanding and organizing the data is crucial at this stage. Once the data is organized, it’s easier to plot it on the x and y-axes.
The next step would be defining the x-axis (usually time) and y-axis (the parameter you are studying). Following this, points should be plotted on the graph based on the collected data. The scale of the graph should be carefully defined to avoid any misleading visualization of changes.
Once the points are plotted, a smooth curve, known as a spline, is drawn to connect these points. An important aspect here is ensuring the curve accurately reflects the ups and downs in the data to maintain data integrity.
Finally, the chart is made more legible by adding labels to the axes, a title to the chart, and a legend if necessary. Optimum color schemes can be selected to separate different sets of data visually or to highlight particular points.
Useful Techniques To Improve Your Spline Chart
Improving your spline chart involves utilizing a few simple techniques. First, consider zooming in on areas of interest: this allows for a detailed study of a particular period. Moreover, a zoomed-in view lessens data density and opens up the graph for clearer understanding.
Secondly, consider using interactive features whenever possible. Modern charting tools often come with the capability to animate the chart, add tooltips for specific data points, and allow the viewer to interact with the graph.

Thirdly, where appropriate, use a logarithmic scale in complex charts. Logarithmic scales can compactly represent large ranges of values, making the chart more readable.
Lastly, consistency is key. If you’re producing a series of charts, ensure they all follow the same design rules for easier comparison. This includes maintaining the same color scheme, scale, font size, and positioning of labels across the graphs.
Altogether, creating a clear and concise spline chart requires some knowledge and practice but can be an invaluable tool in data analysis. Remember to keep the chart clean and focused, use consistent and meaningful colors, and label all charts comprehensively.